Configuring a New SoftNAS Instance on EC2
You can configure a new SoftNAS instance on EC2 from the Amazon Web Services Console. You can either leverage the Free Usage Tier to launch and use a free Amazon EC2 Micro instance for 12 months, or you can launch a larger instance type.
Creating a new SoftNAS instance on EC2 is very easy.
The important steps involved in creating a new SoftNAS instance are given below.
Creating a New Instance
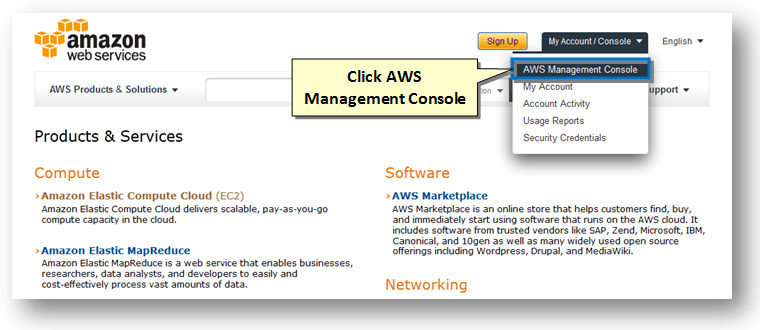
1. Access Amazon Web Services from your browser. Click the Sign Up button or choose AWS Management Console option in the My Account / Console menu in the top right corner of the screen.
The Amazon Web Services Console will be displayed.
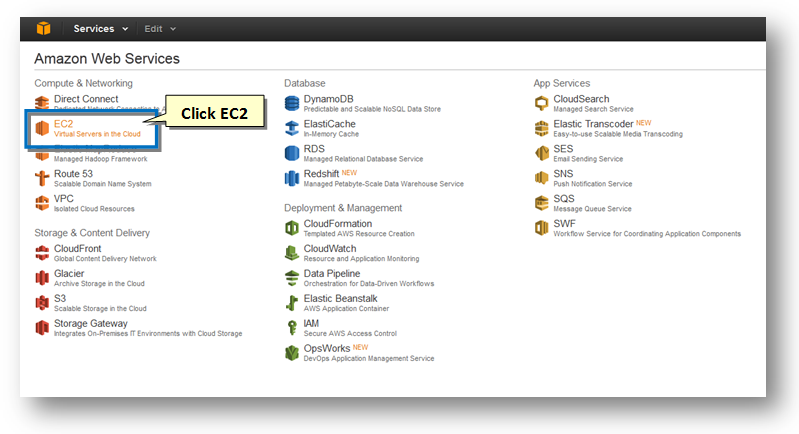
2. Click the EC2 option on the console to create a SoftNAS virtual server in the cloud.
The Amazon EC2 Console Dashboard will be displayed.
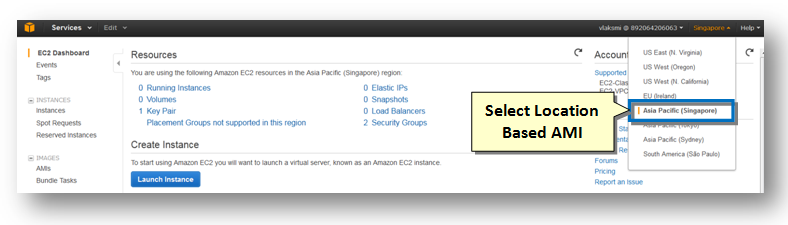
3. Select the location / region for SoftNAS AMI on EC2 from the top right drop down list. In the above example, the Asia Pacific (Singapore) AMI is selected.
The Create a New Instance Wizard will be displayed.
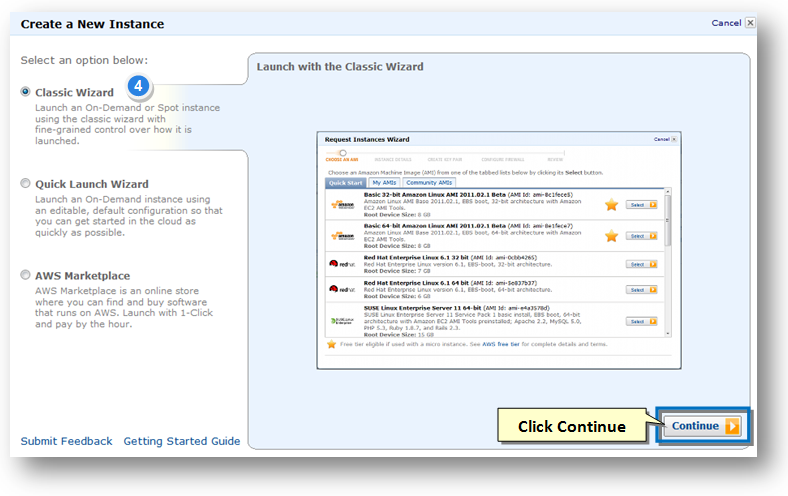
4. By default the Classic Wizard option is selected.
5. With the Classic Wizard option selected, click the Continue button at the end of the wizard.
The Request Instances Wizard willl be displayed for selecting the AMI.
In the next step, you will select the SoftNAS AMI.
Choosing an AMI
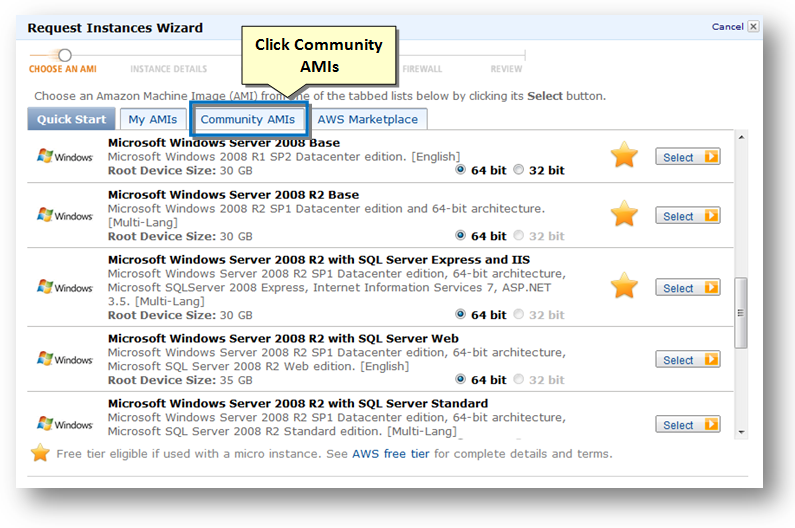
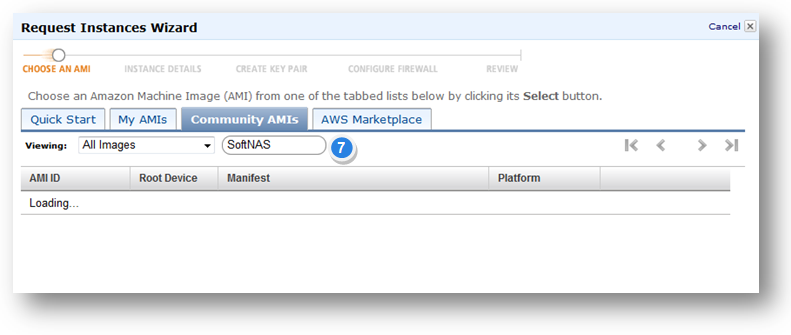
6. Click the Community AMIs tab (hint: choose "Public Images" to reduce the search time)
7. Enter the name as "softnas" in the search box for searching the required AMI..
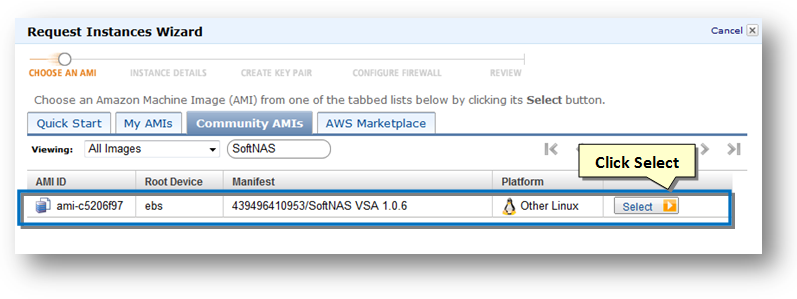
It will take some time for the SoftNAS instance to show up and finally, the region based SoftNAS AMI will be shown in the search results.
Note: The actual "Manifest" value will vary with different releases of SoftNAS and may not match exactly as shown above.
8. Click the Select button to select the AMI.
The Instance Details section of the wizard will be displayed.
Providing Instance Details
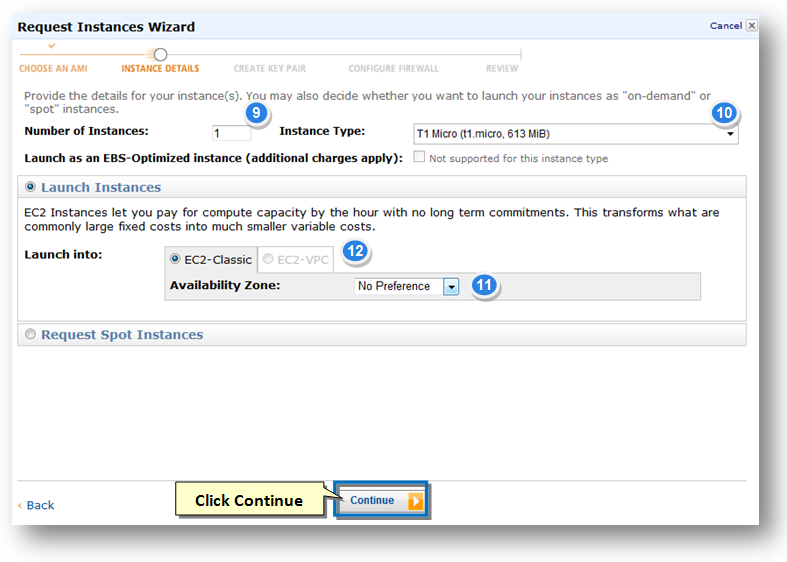
9. Enter the number of instances as 1 in the Number of Instances text entry box.
10. Select the type of instance from the Instance Type drop down list.
11. Select the zone available from the Availability Zone drop down list.
12. Depending on the instance type selected, you can also check the instance that can be launched as an EBS-Optimized instance for more consistent and predictable performance in the Launch Into field.
VPC Notes: The Launch into option defaults to EC2; however, you can also launch an instance into your own Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) environment instead. VPC's can be useful if all of your computing will be done in the EC2 environment, or if you want to interconnect an existing network via a VPN gateway to the VPC environment; e.g., setting up an IPSec tunnel between an existing data center and the VPC. If you choose to operate SoftNAS within the private subnet of a VPC, please note that you must create an outbound NAT route that enables the SoftNAS instance to access the Internet to perform software updates, activation, etc. In this case, only outbound TCP traffic to the softnas.com domain is required to be enabled; i.e., inbound access to ports 22, 80 and 443 for administration can be restricted to VPC subnet access only.
13. Click the Continue button.
The Instance Details section of the wizard will be displayed.
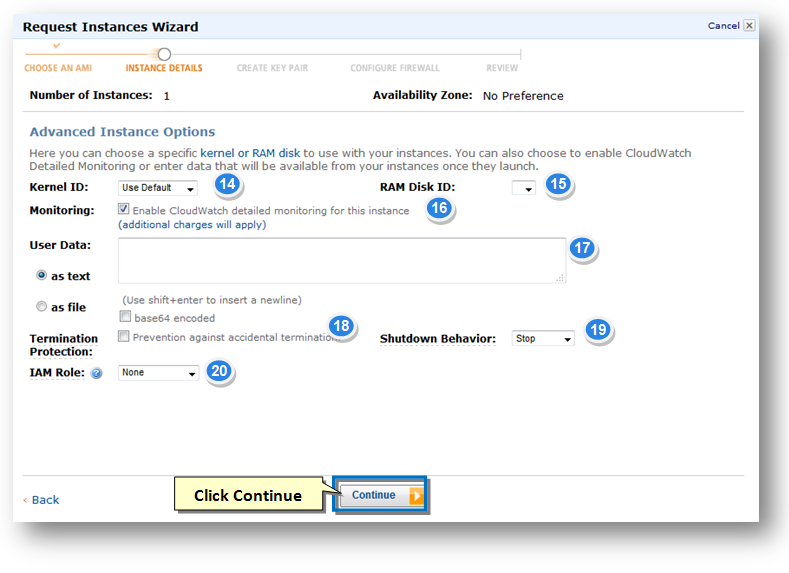
14. Accept the default value for the kernel for the Kernel ID.
15. Accept the default id from the RAM Disk ID.
16. CloudWatch provides a detailed monitoring of the SoftNAS instance. The Free Tier includes basic monitoring metrics at 5-minute intervals, 10 monitoring metrics, 10 alarms and 1 million API requests at no additional charge. Check the box in the Monitoring field to enable CloudWatch, which is recommended.
17. Check the box Prevention against accidental termination option in the Termination Protection field. This prevents accidental termination of the SoftNAS instance. When an instance is terminated, it is permanently deleted, so this additional termination protected is highly recommended.
18. Select the type of shutdown behavior from the Shutdown behavior drop down list. This option allows you to select whether the instance should stop or terminate when shut down.
19. The AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role helps you to associate with the instance. Currently select the role as None from the IAM Role drop down list.
20. Click the Continue button.
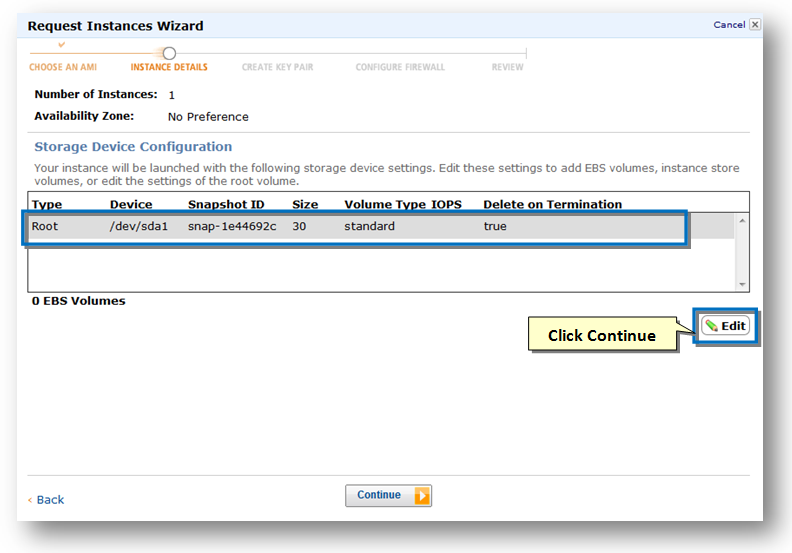
The Storage Device Configuration section of the wizard will be displayed.
By default, you will see the SoftNAS 30 GB device, as shown above. The root device is an EBS volume used to boot and run SoftNAS.
At this point, you may simply choose to continue without configuring any additional storage and add storage disks later (recommended if you are creating a production instance).
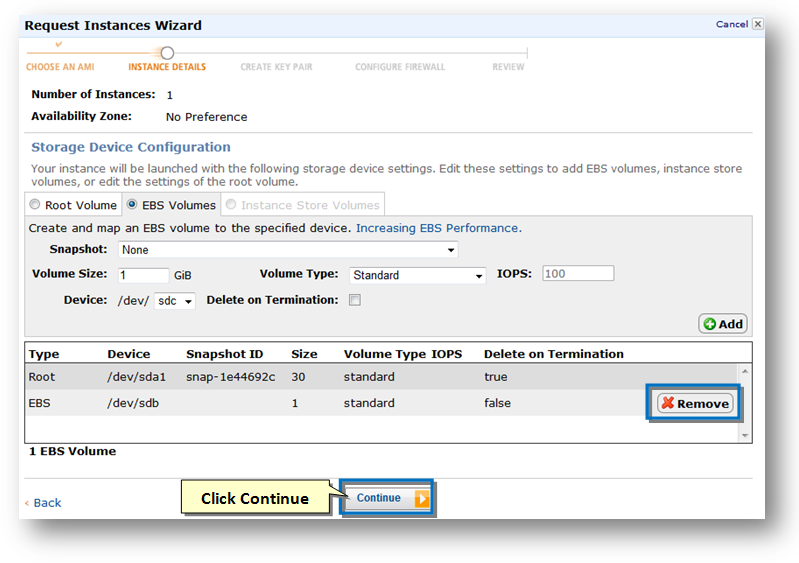
21. If you prefer to add some data disks for SoftNAS now, select the instance and click the Edit button. This helps you to add EBS volumes, instance store volumes or edit the settings of the root volume.
The Storage Device Configuration will now be displayed in edit mode.
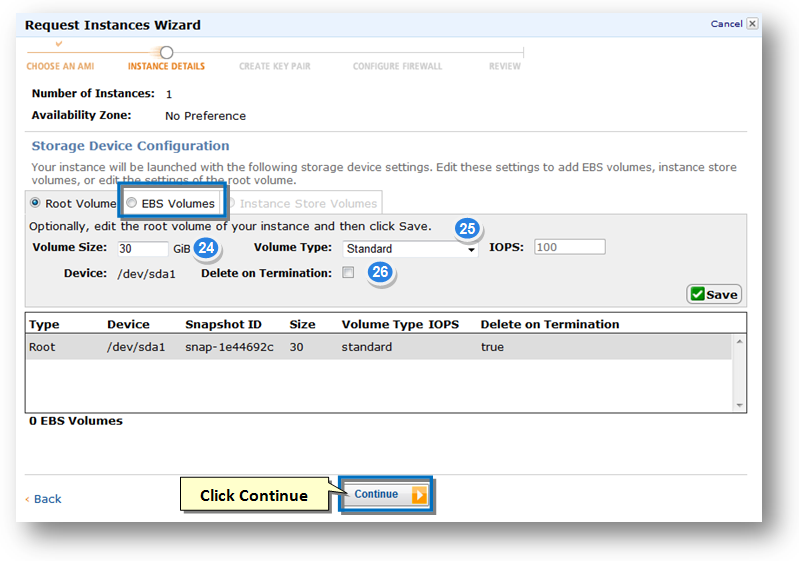
22. Navigate to the EBS Volumes tab. These EBS volumes will serve as raw disk storage for SoftNAS, and can later be configured as RAID groups within SoftNAS.
Continue attaching the EBS volumes. The EBS Volumes will be attached to an EC2 instance to provide persistent data storage.
For example, if you wanted 1 TB of usable storage with RAID redundancy for increased performance and data redundancy, you could configure:
-
Two 1 TB EBS volumes, configured as RAID 1 mirrors
-
Five 250 GB EBS volumes, configured as RAID 5 (four data, single parity)
-
Seven 250 GB EBS volumes, configured as RAID 6 with a spare (four data, dual parity, one spare)
23. Enter the size of the EBS volume in the Volume Size text entry box.
24. Select the type of volume from the Volume Type drop down list. The available options are Standards and Provisioned IOPS (io1).
-
Standard: Default IOPS (no guaranteed IOPS level in shared environment - less predictable, less consistent performance)
-
Provisioned IOPS: assign a specific level of IOPS by entering the number of I/O per second you want assured for the EBS data volumes (see Choosing an Instance Type)
25. Make sure to uncheck the box in the Delete on Termination field.
Note: This is very important because in the event the SoftNAS instance is terminated for any reason, even the EBS data volumes will be delted. To avoid the possibility of data loss, it is better to uncheck this field.
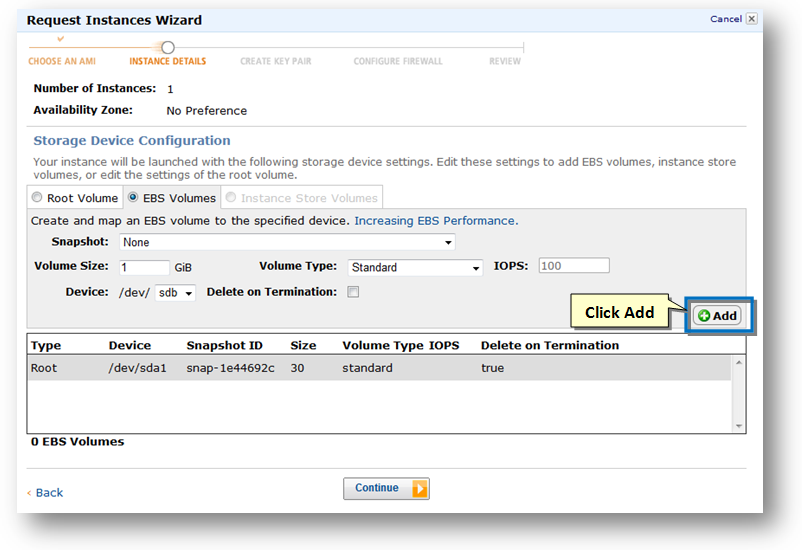
26. Click the Add button to add new EBS volume and map it to the specified device.
Note: the device will default to /dev/sdf. For second and subsequent devices, you must manually enter the next sequential device ID; e.g., /dev/sdg, /dev/sdh, etc.
Use device names of the format /dev/sdf[1-15] to /dev/sdp[1-5] instead; e.g., /dev/sdf1, /dev/sdf10, /dev/sdp15. This naming approach provides access to the most EBS volume disk devices. Do not mix the base name devices (e.g., /dev/sdg) with the numeric device names (/dev/sdg12). If you use a base device name, it will prevent use of the numeric device names, so use of the base names is no longer recommended.
27. Click the Continue button.
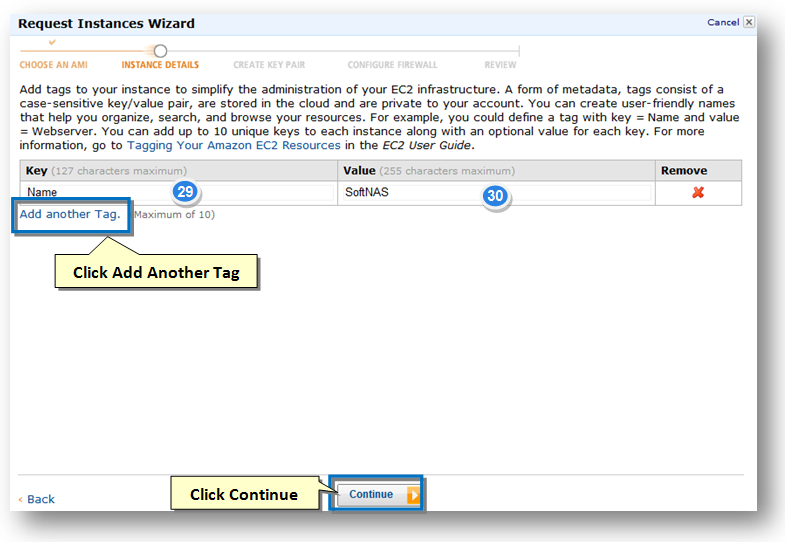
In the next step, you can add tags to your instance and this helps in organizing, searching and browsing your resources.
28. Enter the name of the tag in the Key field.
29. Enter the value for the tag in the Value field.
30. You can add more tags by clicking the Add Another Tab button.
31. Once all the tags are defined, click the Continue button.
Creating a Key Pair
The Create Key Pair section of the wizard will be displayed. In this step, you will create a public/private key pair used with SSH to access and administer your SoftNAS instance in the cloud.
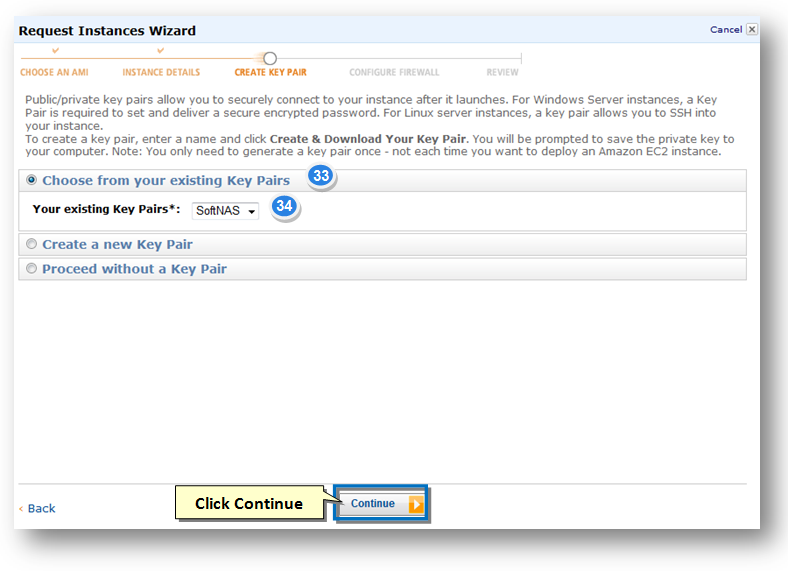
32. The Key Pair helps you to securely connect to your instance when it is launched. You can either choose from existing key pairs that you have created in the current region or create a new key pair. In the example, the option, Choose from your existing Key Pairs is selected.
33. Select the required key pair from Your Existing Key Pairs drop down list.
Note: You should not select the Proceed without a Key Pair option. If you launch an instance without a key pair, you will not be able to connect to it. This option is used only when you are creating your own AMI and don't need to connect to the instance.
34. Click the Continue button.
Configuring Firewall
In the next step of configuring the firewall, you will create security group that defines firewall rules for your instances. These rules specify which incoming network traffic is delivered to your instance. All other traffic is ignored.
Security groups contain rules which determine which types of inbound traffic (TCP, UDP, ICMP) and ports are allowed. A Security Group is then assigned to an instance(s) to manage the inbound traffic flow.
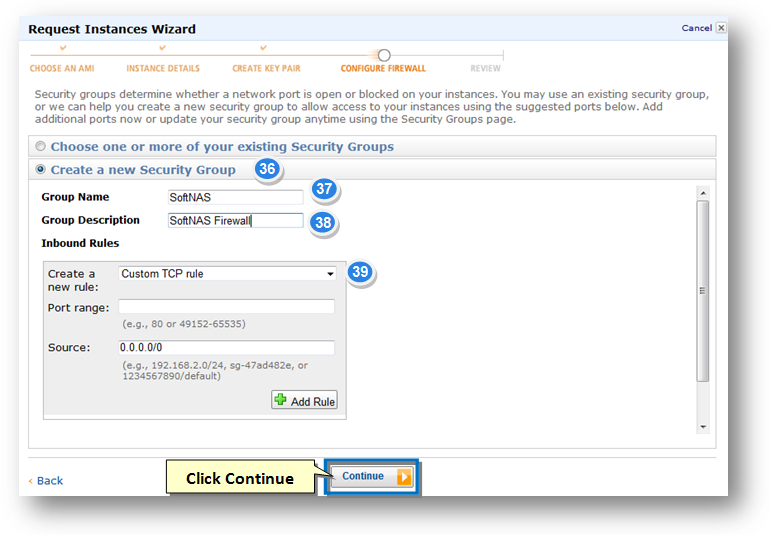
35. Check the box in the Create a New Security Group field.
36. Enter the name of the security group in the Group Name text entry box.
37. Enter the description for the scurity group in the Group Description text entry box.
38. In the Inbound Rules section, select Custom TCP Rule from the Create a New Rule drop down list. Configure Port Range and Source. Similarly, create rules for ICMP, SSH, HTTPS and HTTP.
Consider the following Security Group configuration:
The following ports are opened for inbound traffic:
-
22: SSH allows incoming secure shell connections (required to administer SoftNAS / EC2 instance running Linux)
-
80: HTTP allows incoming web traffic
-
443: HTTPS is required to administer SoftNAS
Additional ports will need to be opened for NFS, CIFS, iSCSI, etc. as appropriate. An ICMP "reply" rule can also be added to allow ping responses.
Note The Source is configured to 0.0.0.0/0 (not recommended), which means allow access from any IP address on the Internet. In practice, it would be preferred to limit the range of IP addresses to only those absolutely required to have SoftNAS access. For example, SSH access should be limited to only those source IP addresses required to administer the system over the Internet, as you don't typically want just anyone being able to connect to SoftNAS.
40. Click the Continue button.
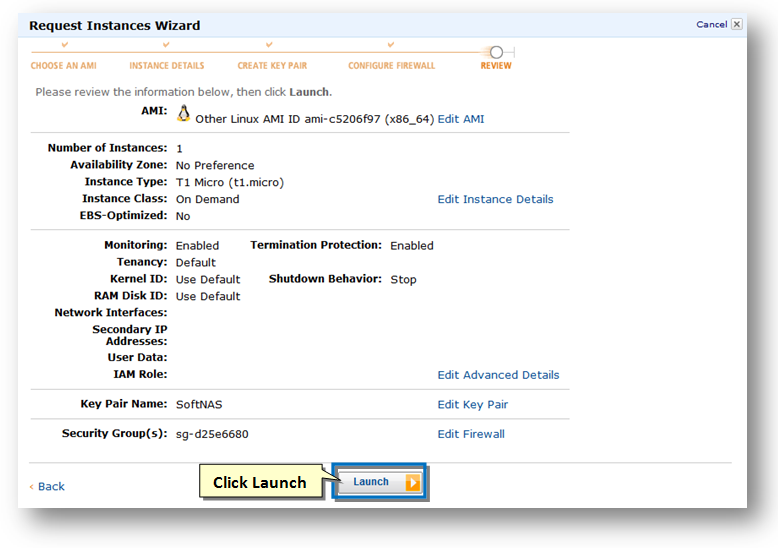
Reviewing Details
In the Review step, you can review all the information related to the instance before launching it.
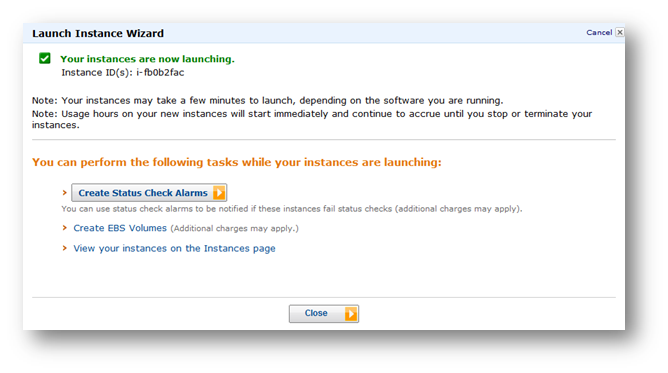
41. Once you have reviewed all the information, click the Launch button.
The SoftNAS instance will take few minutes for launching. Within some 90 seconds, your SoftNAS instance will be created.
For more information, refer to the following sections.