Add Raw Device Mapping in VMware
Raw Device Mapping (RDM) is one way to pass a raw disk device directly through from the disk controller to the SoftNAS VM in VMware. Older VMware documentation indicates RDM is not supported by locally-attached devices, which is no longer the case; however, like many things in VMware administration, local RDM devices must be configured partially using command line tools.
Use an RDM for direct SSD access, especially for write logs, in order to improve synchronous write speeds (especially for small block synchronous writes like 4K blocks used by VMware and many databases). Normally VMFS works great for creating storage VMDK's for SoftNAS, but for small block sync writes, the VMFS 1 MB block size gets in the way. RDM provides the SoftNAS VM with direct access to the raw SSD SCSI interface, providing the fastest possible write log.
Configuring Raw Device Mapping (RDM) in VMware
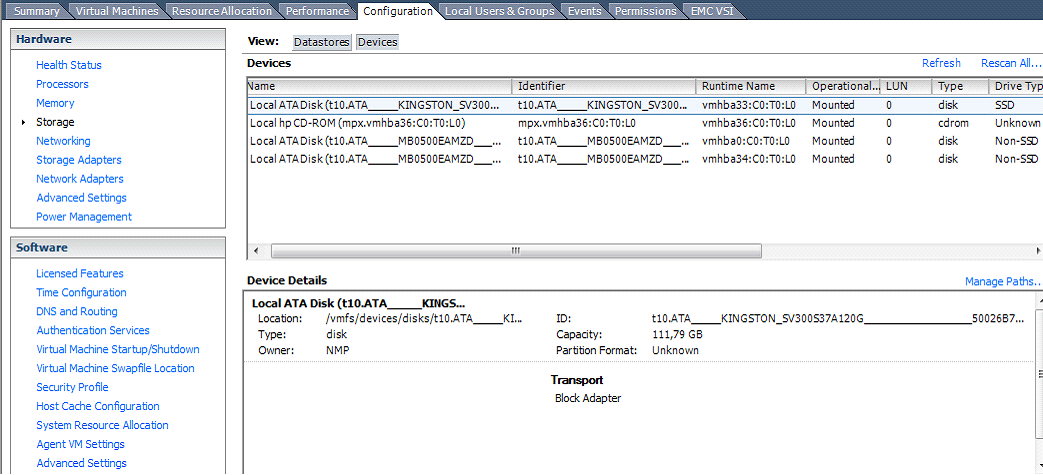
1. Open the vSphere client click on the VMware host on configuration tab under storage in the devices find the identifier of the SSD hard disk, as shown below.
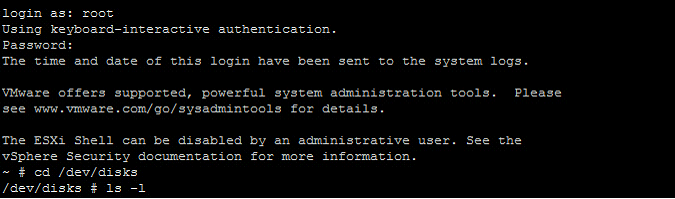
2. Connect to the ESXi host with ssh and cd /dev/disks.
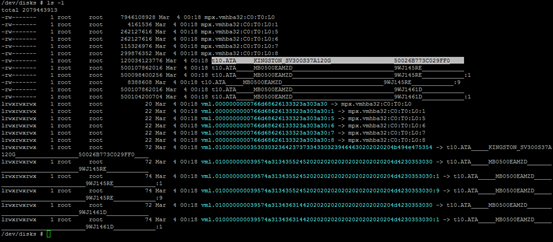
3. Enter "ls –l" command to see all the devices and identify the SSD disk
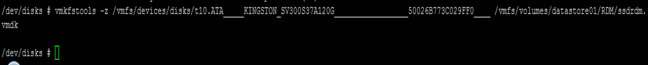
4. To configure the device as an RDM and output the RDM pointer file to your chosen destination, run the command:
# vmkfstools -z /vmfs/devices/disks/<diskname> /vmfs/volumes/<datastorename>/<vmfolder>/<vmname>.vmdk
In our case we have the following:
5. Now that we have create RDM we must assigned it to our VM.
Right click on the SoftNAS vm edit settings ADD tab, Select Hard disk and press Next.
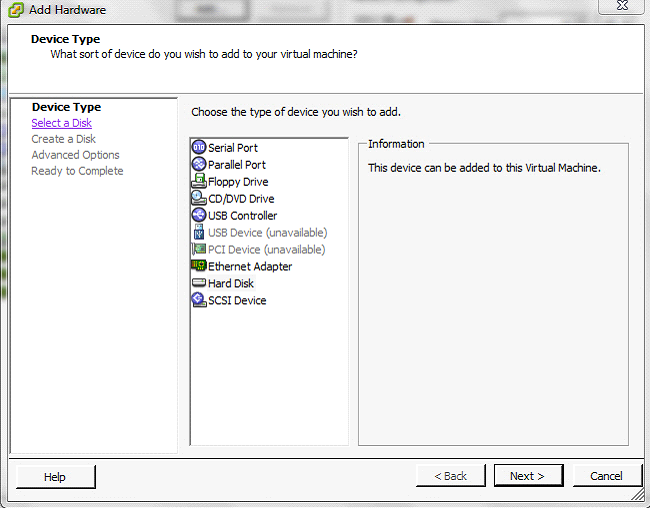
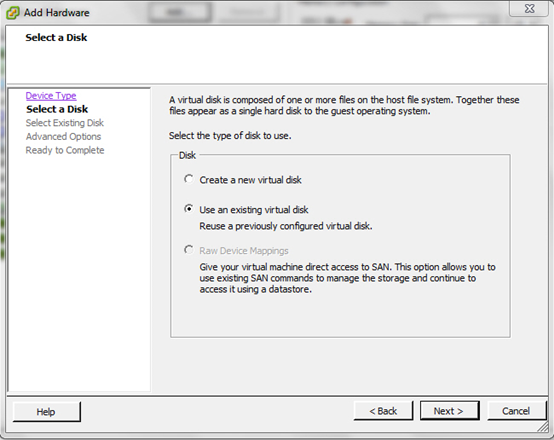
6. Next, choose the existing virtual disk option and press Next.
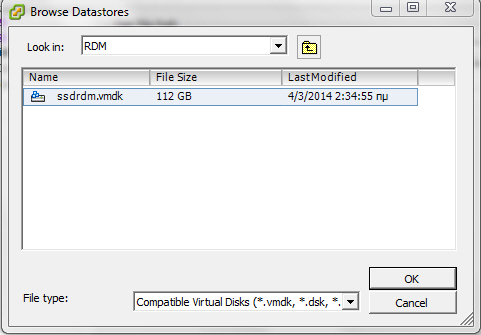
7. Browse to the location you have the RDM pointer stored and choose it, then press OK.
You should now see your new hard disk in the virtual machine inventory as Mapped Raw LUN
At this point, you have mapped the raw SSD device to the SoftNAS VM.